Introduction
MySQL is a popular database management system for web application software. Like many web services, MySQL has an administrator-level or root password. The root password allows a user to perform all top-level functions in the database.
If you've never set a root password on your MySQL database, you should be able to connect to it. However, this is not a good security practice, as anyone can access your database.
If your database has a root password, but you lost track of it, this guide will help you reset a MySQL root password on Linux and Windows.

Prerequisites
- An existing MySQL database.
- Access to a Linux or Windows server running MySQL.
- Administrator privileges.
- A text editor.
- Access to a command-line interface (or terminal).
How to Change MySQL User Root Password in Linux
Follow the steps outlined below to change your MySQL root password in Linux. For this tutorial, we will use Ubuntu 22.
Step 1: Log in as MySQL User
Log into your system as the user that you use to start and run the MySQL server. You can also log in as root, but in that case, you must use the --user=mysql -p option when starting the mysqld service later in step 5.
Starting the server as root creates root-owned files in the data directory, which can cause permission-related issues for future server startups.
Step 2: Stop the MySQL Server
Before changing the password, stop the MySQL server if it is active. Run the following command to stop the mysqld process:
sudo service mysql stopThe command stops the MySQL server. Alternatively, run the following command to kill all running instances of the MySQL server:
killall mysqldStep 3: Create a Password File
Create a file in which you will specify the new password. Follow the steps below:
1. Create a new text file using your favorite text editor. In this tutorial, we will use nano. The syntax is:
sudo nano /home/[username]/mysql-initReplace [username] with your actual username on your system.
2. Next, add the following line to the file:
ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'NewPassword';- Replace the
NewPasswordwith the password you want to use. Include the single-quote marks and the semicolon at the end. Make sure to use a strong and secure password. - The command works for the machine you're currently using. Replace
localhostwith the appropriate hostname if you're connecting to a different system.

3. Save the file with Ctrl+O and exit the editor with Ctrl+X. If you are not logged in with the user account that you use for running the server, set the file permissions to allow the MySQL user to read the file.
Step 4: Apply the Changes
To apply the password change, use the following syntax:
sudo mysqld --init-file=/home/[username]/mysql-init &Make sure to replace [username] with your actual username on your system. For example:

The command applies the text-file password change. The output shows the process ID (PID) of the service that was started in the background.
Step 5: Restart the Server
Restart the MySQL server after changing the root password to apply the changes. Enter the command below:
sudo service mysql startWait until the process completes.
Step 6: Log in and Clean Up
Log into your MySQL server using the root account and verify the new password works.
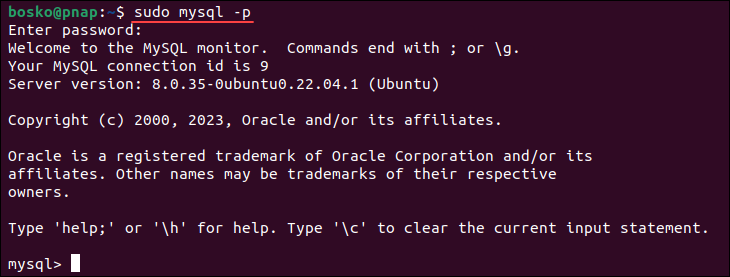
If everything works, you can delete the file you created in Step 3.
How to Reset MySQL Root Password in Windows
The steps below show how to reset the MySQL root password in Windows. In this tutorial, we will use Windows 11, but the process works for Windows 10 as well.
Step 1: Log in as Administrator
Log in to the Windows machine as an administrator. Administrative access ensures that you have the necessary rights to modify system-level settings.
Step 2: Stop MySQL server
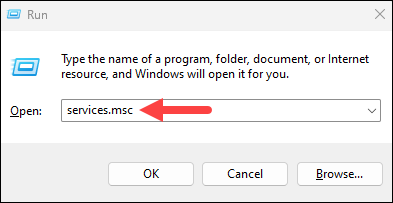
1. Press Win+R (hold the Windows/Super key, and press r).
2. In the Run box, type services.msc and press Enter.
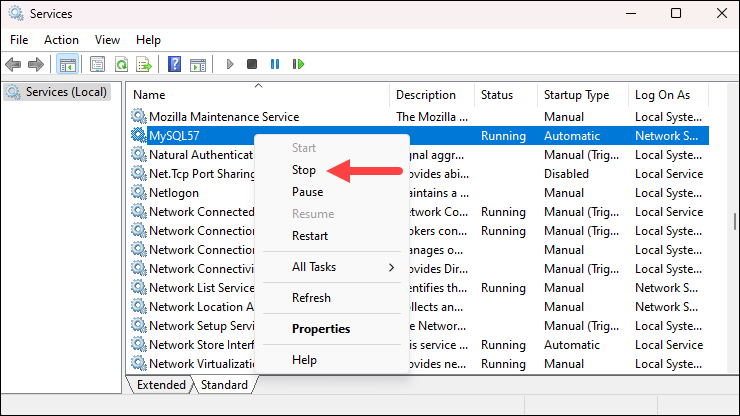
3. Scroll down the list of services to find the MySQL service. Right-click the entry and select Stop.
Step 3: Create Password File
The password file is a .txt document containing the new password you want to use. Follow the steps below:
1. Press the Windows key and search for Notepad. Press Enter to open the app.
2. Add the following line to the text file:
ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'NewPassword';- Make sure to keep the quote marks and semicolon. Replace
NewPasswordwith the password of your choice. - The
localhoststring makes the password change on your local system. If you’re changing the password on a system over the network, substitutelocalhostwith the appropriate hostname.
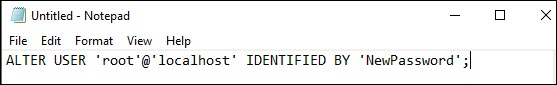
3. Save the file to the root of your hard drive (C: ). The filename should be mysql-init.txt.
Step 4: Open Command Prompt
1. Press the Windows key and type cmd.
2. From the search results, select the Run as administrator option to open Command Prompt as administrator.
Step 5: Add New Parameters and Restart Server
1. Navigate to the MySQL directory using the command prompt:
cd "C:\Program Files\MySQL\MySQL Server 5.7\bin"If you have a different MySQL version, make sure to use that version in the command.
2. Depending on how you installed MySQL, there are two ways to restart the server with the new parameters:
- If you installed MySQL using the ZIP archive
Run the following command
mysqld --init-file=C:\\mysql-init.txtNote that there are two slashes after the C: prompt.
- If you installed MySQL using the MySQL Installation Wizard
You must specify a --defaults-file option in the command, followed by the path to the configuration file. Find the file path by right-clicking the MySQL service in the services list and selecting Properties:
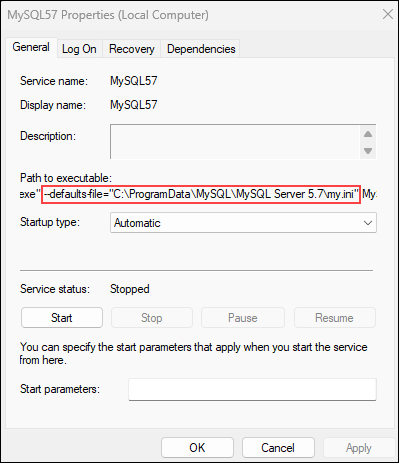
The file path is listed in the Path to executable section. Copy the file path and use it in the command below, but make sure to use double slashes (\\) instead of single (\) in the path:
mysqld --defaults-file="C:\\ProgramData\\MySQL\\MySQL Server 5.7\\my.ini" --init-file=C:\\mysql-init.txt3. Restart the MySQL service from the Services list. Right-click the MySQL service and select Start.
Step 6: Clean up
Now, log into your MySQL server as root using the new password. Once MySQL launches and you've confirmed the password change, delete the C:\mysql-init.txt file.
Conclusion
After reading this guide, you should be ready to reset the root password on MySQL in Linux and Windows. Whether you forgot your password or just want to change it for security reasons, it is an easy task that improves your database security.
Next, learn the difference between MySQL and PostgreSQL, or follow our guide and get started with MySQL Workbench on Ubuntu.